Chemical Reactions
Chemistry is boring without reactions; everything just sits there. There are only 50 or so elements of which we routinely make use, but a practically infinite number of ways in which to combine those to make new materials with different, sometimes unexpected properties. We're still finding ways to put elements and compounds together (synthesis) and to take them apart (decomposition). Those processes necessarily involve reactions.
This section will review some elementary reaction types, then we'll talk about some more complex kinds. Many of the reactions written below contain numerical coefficients in front of molecules, like 2H2O, which simply means "two molecules of water. Don't worry too much about those for now, you'll learn more when you learn to balance chemical equations.
Shortcuts to reaction types
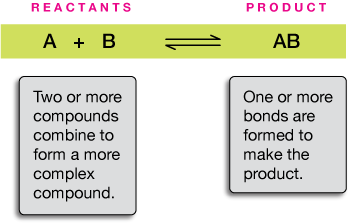
The reaction in the green box below is a prototype (that means A's and B's stand for elements) of a typical synthesis reaction, a reaction in which atoms or smaller molecules combine to form one or more larger or more complicated compound(s).
Before we go on to some examples, let's use this reaction to take care of some basic reaction terminology. The compound(s) on the left are called reactant(s). Those on the left are product(s). We separate different sets of reactants and products with + signs.
About arrows →
We generally only use a single arrow ( $\longrightarrow$ ) to indicate a few reactions where the reverse reaction is very improbable, like the dissociation of a strong acid.
More often we use a double arrow ( $\rightleftharpoons$ ) to show that the reaction actually proceeds in both directions at the same time. There will be more to say about that in the section on equilibrium, but for now, you should start using the double arrow to write most reactions.
Examples of synthesis reactions
Here are a few examples of synthesis reactions. Compare them to the model reaction above to make sure you get the idea. For each reaction there's a version written in an English sentence on the right, so that you might be able to pick up on the meaning more easily:
| Reaction | What it means |
|---|---|
| $Fe \; + \; O_2 \; \rightleftharpoons \; FeO_2$ | Iron combines with oxygen to form iron oxide |
| $H_2 \; + \; Br_2 \; \rightleftharpoons \; 2 \; HBr$ | Diatomic hydrogen combines with diatomic bromine to form two molecules of hydrogen bromide |
| $2 \; NH_3 \; + \; H_2 O \; + \; CO_2 \; \rightleftharpoons \; (NH_4)_2 CO_3$ | Two molecules of ammonia, a water and a carbon dioxide combine to form a molecule of ammonium carbonate. |
| $CaO \; + \; SO_2 \; \rightleftharpoons \; CaSO_3$ | Calcium oxide and sulfur dioxide react to form calcium sulfite. |
Synthesis reactions
In a synthesis reaction, two or more simpler components are joined to form a more complex compound.
Solids, liquids & gases
Often we write the state (solid, liquid, gas, aqueous) of a compound in a reaction using parenthesis and the letters (s), (l), (g) & (aq). Aqueous solutions are solutions in which water is the solvent. They are so ubiquitous in our chemistry that they get the special designation (aq). Here's the table above, rewritten with the added state information:
| $Fe_{(s)} \; + \; O_{2 \, (g)} \; \rightleftharpoons \; FeO_{2 \, (s)}$ | solid Iron combines with oxygen gas to form solid iron oxide |
| $H_{2 \, (g)} \; + \; Br_{2 \, (g)} \; \rightleftharpoons \; 2 \; HBr_{(g)}$ | Hydrogen gas combines with bromine gas to form two molecules of gaseous hydrogen bromide |
| $2 \; NH_{3 \, (g)} + H_2 O_{(l)} + CO_{2 \, (g)} \rightleftharpoons (NH_4)_2 CO_{3 \, (aq)}$ | Two molecules of gaseous ammonia, a liquid water molecule and a molecule of carbon dioxide gas combine to form a molecule of aqueous ammonium carbonate. |
Aqueqous (ā' · kwee · us) solutions are mixtures of soluble ionic or nonionic compounds and water. They are pure substances.
Decomposition reactions are really just the opposite of synthesis. Something more complicated "falls apart" into less complicated things. Decomposition is usually what we're talking about when we speak of "shelf life", like for drugs or some foods.
Decomposition that is catalyzed by visible or ultraviolet light is why many drugs come in brown plastic bottles (the brown color blocks a lot of visible light and plastics absorb most UV).

Examples of decomposition reactions
| $AgO_{2 \, (aq)} \; \rightleftharpoons \; Ag_{(s)} \; + \; O_{2 \, (g)}$ | Aqueous silver oxide decomposes into solid silver metal and oxygen gas. |
| $H_2 SO_{4 \, (aq)} \; \rightleftharpoons \; 2 H^+_{(aq)} \; + \; SO^{2-}_{4 \, (aq)}$ | Sulfuric acid dissociates into two protons plus a sulfate ion. |
| $H_2 O_{2 \, (aq)} \; \rightleftharpoons \; H_{2 \, (g)} \; + \; O_{2 \, (g)}$ | Aqueous hydrogen peroxide decomposes into hydrogen and oxygen gas. |
Displacement reactions might also be called substitution reactions. In a displacement reaction, one chemical moiety from one reactant takes the place of another in the other reactant.
You can think of single-displacement reactions as ones in which a molecule donates part of itself to another atom or molecule. Here's the picture →

Moiety
moy' · it · ee
The word moiety is sometimes used in chemistry to identify one reactant or product.
Literally, it means each of the two parts into which a thing can be divided.
Examples of single-displacement reactions
| $Cu_{(s)}+2 \, AgNO_{3 \; (aq)} \rightleftharpoons CuNO_{3\; (aq)} + 2 \, Ag_{(s)}$ | When solid copper and aqueous silver nitrate react, copper replaces silver in the nitrate compound, with solid silver remaining as a product. |
| $Fe_{(s)}+2HCl_{(g)} \rightleftharpoons FeCl_{2 \; (aq)} + H_{2 \; (g)}$ | When solid iron is treated with hydrochloric acid, two chlorines from the acid combine with iron to form iron (II) chloride and hydrogen gas. |
| $2 \, Al_{(s)}+Fe_2O_{3 \; (aq)} \rightleftharpoons Al_2O_{3 \; (aq)}+2Fe_{(s)}$ | Two aluminum atoms react with one atom of Iron (III) oxide in aqueous solution to form aluminum (III) oxide and solid iron. |
The double displacement reaction is a pretty obvious extension of single displacement. It requires two binary compounds, each of which exchanges one of its parts with the other. Once you understand double displacement, it's possible to imagine all kinds of displacement reactions in which more complicated compounds swap one or more parts. Here is the double displacement model:

Examples of double-displacement reactions
| $Pb(NO_3)_{2 \; (aq)}+2 \, NaCl_{(aq)} \rightleftharpoons 2 \, NaNO_{3 \; (aq)}+PbCl_{2\; (s)}$ | Lead (II) nitrate reacts with the salt sodium chloride to produce sodium nitrate and lead (II) chloride. |
| $H_2SO_{4 (aq)}+2 \, LiOH_{(aq)} \rightleftharpoons Li_2 SO_{4 \; (aq)}+2 H_2O_{(l)}$ | Aqueous sulfuric acid reacts with lithium hydroxide to produce lithium sulfate and water. |
| $AgNO_{3 \; (aq)}+HCl_{(g)} \rightleftharpoons AgCl_{(s)}+HNO_{3 (aq)}$ | Aqueous silver nitrate reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce a solid precipitate of silver chloride and aqueous nitric acid. |
Acids and bases are covered in another section, so this kind of reaction might seem a little fuzzy. You can come back to it later. For now, consider an acid to be an ionic compound that yields H+ ions and a base to be an ionic compound that yields OH- ions. Excess H+ ions are what make a solution acidic and excess OH- ions are what makes it basic. OH- and H+ can react to form H2O, which is (exactly) neither acidic nor basic—water is, by definition, neutral.
The products of neutralization are always a salt (a non-acidic, non-basic ionic compound) and water. Here's what it looks like:

Examples of acid-base neutralization reactions
| $HCl_{(aq)}+NaOH_{(aq)} \rightleftharpoons NaCl_{(aq)}+H_2O_{(l)}$ | Hydrochloric acid is neutralized with an equimolar amount of sodium hydroxide in aqueous solution, forming the salt NaCl and liquid water at pH 7. |
| $H_3PO_{4 \; (aq)} + 3 \, KOH_{(aq)} \rightleftharpoons K_3PO_{4 \; (aq)}+3 \, H_2O_{(l)}$ | Phosphoric acid is completely neutralized with potassium hydroxide to form potassium phosphate and liquid water. |
| $ \begin{align} 2 \, HCOOH_{(aq)} &+Ba(OH)_{2 \; (aq)} \rightleftharpoons \\[5pt] 2 \, HCOOBa_{2 \; (aq)} &+ 2H_2O_{(l)} \end{align}$ | Formic acid (HCOOH) is neutralized with barium hydroxide to yield barium formate (a salt) and water. |
Writing neutralization reactions — identifying the salt
Here's a trick for identifying the products in acid-base neutralization reactions. Let's say you want to write a reaction for the neutralization of perchloric acid, $HClO_4$, and calcium hydroxide, $Ca(OH)_2$.
First write dissociation reactions for the acid and base. These are really just decomposition reactions; salts like these tend to come apart into separate ions when placed in water. Here are the reactions:
Acid
$$HClO_4 \longrightarrow H^+ + ClO_4^-$$
Base
$$Ca(OH)_2 \longrightarrow Ca^{2+} + 2 \, OH^-$$
Now we know that one of the products is $H_2O$. that's obviously going to be formed from the $H^+$ and $OH^-$ ions, so the salt is just a combination of the remaining ions, $Ca^{2+}$ and $ClO_4^-$, in the right proportions to make a neutral compound,
$$Ca(ClO_4)_2$$
Having a list of common molecular (polyatomic) ions around will help, too.
Combustion is rapid oxidation or burning. It is the (usually) rapid combination of oxygen with a hydrocarbon (composed only of C and H) or an oxy-hydrocarbon (also contains oxygen). Combustion generally releases a great deal of the energy stored in the chemical bonds of a molecule.
The model reaction below is a general form for balancing any hydrocarbon reaction. It's interesting, but I wouldn't spend any time trying to memorize it. It's better just to learn to balance any kind of reaction quickly and be done with it.

Examples of combustion reactions
| $CH_{4 \; (g)}+2 \, O_{2 \; (g)} \rightarrow CO_{2 \; (g)} + 2H_2O_{(g)}$ | Methane (CH4) gas is combusted in the presence of oxygen to yield carbon dioxide and water. |
| $2 \, C_2H_5OC_2H_{5 \; (l)}+13 \,O_{2 \; (g)} \rightarrow 8 \, CO_{2 \;(g)}+10 \, H_2O_{(g)}$ | Diethyl ether is burned in the presence of oxygen to yield carbon dioxide and water. |
| $2 \, C_6H_{6 \;(g)}+15 \, O_{2 \; (g)} \rightarrow 12 \, CO_{2 \; (g)}+6 \, H_2O_{(g)}$ | Two molecules of benzene (C6H6) are burned in the presence of excess oxygen to yield 12 molecules of CO2 and six molecules of H2O. |
Dimethyl ether, burned in the second reaction above, is an oxy-hydrocarbon. Think of it as a hydrocarbon that carries around a bit of its own oxygen for combustion. In fact, molecules like these can help to ensure that combustion reactions go to completion, especially in unfavorable conditions — like cold weather. Diethyl ether is added to gasoline in some states in winter to help the gas combust fully, avoiding other products that are more harmful to life, such as carbon monoxide (CO).
Some molecules can undergo an internal rearrangement of their structure under certain circumstances. Molecules that have the same number and type of atoms, but different bonding arrangem#ents are called isomers, and interconversion between isomers is called isomerization. Here's an example, the rearrangement of n-butane to isobutane. This diagram is actually a shorthand; I've omitted all of the hydrogens that would be bound to the carbons – each would have to have four bonds.

Here's another example, the rearrangement of a 6-carbon sugar molecule between two forms. →

Practice problems
Determine they type of each reaction below.
-
$NaBr + H_3PO_4 \rightleftharpoons Na_3PO_4 + HBr$
Solution
Combustion: Combines a hydrocarbon with oxygen to produce $CO_2$ and water.
-
$\; NaBr + H_3PO_4 \rightleftharpoons Na_3PO_4 + HBr$
Solution
Double displacement: The ions are $H^+$, $PO_4^{3-}$, $Na^+$, and $Br^-$.
-
$\; Fe^{3+} + 3 \, NaBr \rightleftharpoons FeBr_3 + 3 \, Na^+ $
Solution
Single displacement: The ions are $Fe^{3+}$, $Na^+$, and $Br^-$. The iron ion is substituted for the sodium ion, and the number of bromines has to change because of the difference in cation charge.
-
$\; Mn + O_2 \rightleftharpoons MnO_2$
Solution
Synthesis: Two compounds are joined into one.
-
$\; Na_2CO_3 \rightleftharpoons Na_2O + CO_2$
Solution
Decomposition: One compound breaks into two or more separate compounds.
-
$\; 3 \, Ca(OH)_2 + Al_2(SO_4)_3 \rightleftharpoons 3 \, CaSO_4 + 2 \, Al(OH)_3$
Solution
Double displacement: The ions are $Ca^{2+}$, $OH^-$, $Al^{3+}$, and the molecular ion $SO_4^{2-}$.
-
$\; 2 \, PbSO_4 \rightleftharpoons 2 \, PbSO_3 + O_2$
Solution
Decomposition: The compound on the left breaks into two by losing an oxygen molecule ($O_2$).
-
$\; CaSO_4 + Mg(OH)_2 \rightleftharpoons Ca(OH)_2 + MgSO_4$
Solution
Double displacement: The ions are $H^+$, $SO_4^{2-}$, $OH^-$, and $NH_4^+$.
-
$\; CaSO_4 + Mg(OH)_2 \rightleftharpoons Ca(OH)_2 + MgSO_4$
Solution
Double displacement: The ions are $Ca^{2+}$, $SO_4^{2-}$, $Mg^{2+}$, and $OH^-$.
-
$\; C_2H_4 + O_2 \rightleftharpoons CO_2 + H_2O$
Solution
Combustion: Combines a hydrocarbon with oxygen to produce $CO_2$ and water.
The term "redox" is commonly used to describe oxidation-reduction reactions. Redox reactions are ones in which electrons are transferred from one reactant to another. The reactant that loses electrons is said to be oxidized and the one that gains them is said to be reduced.
I know that sounds a bit like opposite world, but it's a historical artifact that we're stuck with: gaining electrons = "reduction."
We usually write redox reactions in terms of half reactions, representing the oxidation half reaction and the reduction half reaction separately. They can then be added to get the full redox reaction.
For example, the zinc-copper redox reaction looks like this:
$$Zn_{(s)}+Cu_{(aq)}^{2+} \longrightarrow Zn_{(aq)}^{2+} + Cu_{(s)}$$
The oxidation half reaction, in which solid zinc loses two electrons, is
$$Zn_{(s)} \longrightarrow Zn_{(aq)}^{2+} + 2 e^-$$
Notice that in the half reactions we incorporate electrons as a reactant. The reduction half reaction, in which copper ions gain two electrons to convert to solid copper, is
$$Cu_{(aq)}^{2+} + 2 e^- \longrightarrow Cu_{(s)}$$
Two electrons are transferred in each reaction. When the two half reactions are added, there are two electrons on either side of the reaction arrow, and we simply cancel them algebraically.
The sections on electrochemistry and redox balancing will give you a much better look at redox reactions; I present them here just for completeness of this section.

![]()
xaktly.com by Dr. Jeff Cruzan is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. © 2012-2025, Jeff Cruzan. All text and images on this website not specifically attributed to another source were created by me and I reserve all rights as to their use. Any opinions expressed on this website are entirely mine, and do not necessarily reflect the views of any of my employers. Please feel free to send any questions or comments to jeff.cruzan@verizon.net.